The Mac
@TheMac
19 August, 12:15
Notice: Undefined index: tg1tga_access in /home/admin/www/anonup.com/themes/default/apps/timeline/post.phtml on line 396
Linda Moore
@mykismet06350
19 August, 01:16
In response The Mac to his Publication
❤️to let fall in drops❤️
https://www.youtube.com/wa...
https://www.youtube.com/wa...
Notice: Undefined index: tg1tga_access in /home/admin/www/anonup.com/themes/default/apps/timeline/post.phtml on line 396
The Mac
@TheMac
20 August, 04:47
In response Linda Moore to her Publication
IR illuminator flood lights or infrared lights can be used day or night and with black and white cameras to illuminate an area.
Notice: Undefined index: tg1tga_access in /home/admin/www/anonup.com/themes/default/apps/timeline/post.phtml on line 396
The Mac
@TheMac
20 August, 04:48
In response The Mac to his Publication
IR or infrared satellite imagery is sort of a temperature map. The weather satellite detects heat energy in the infrared spectrum (infrared energy is invisible to the human eye). The satellite image displays objects(whether clouds, water or land surfaces) based on the temperature of the object.
Notice: Undefined index: tg1tga_access in /home/admin/www/anonup.com/themes/default/apps/timeline/post.phtml on line 396
The Mac
@TheMac
20 August, 04:49
In response The Mac to his Publication
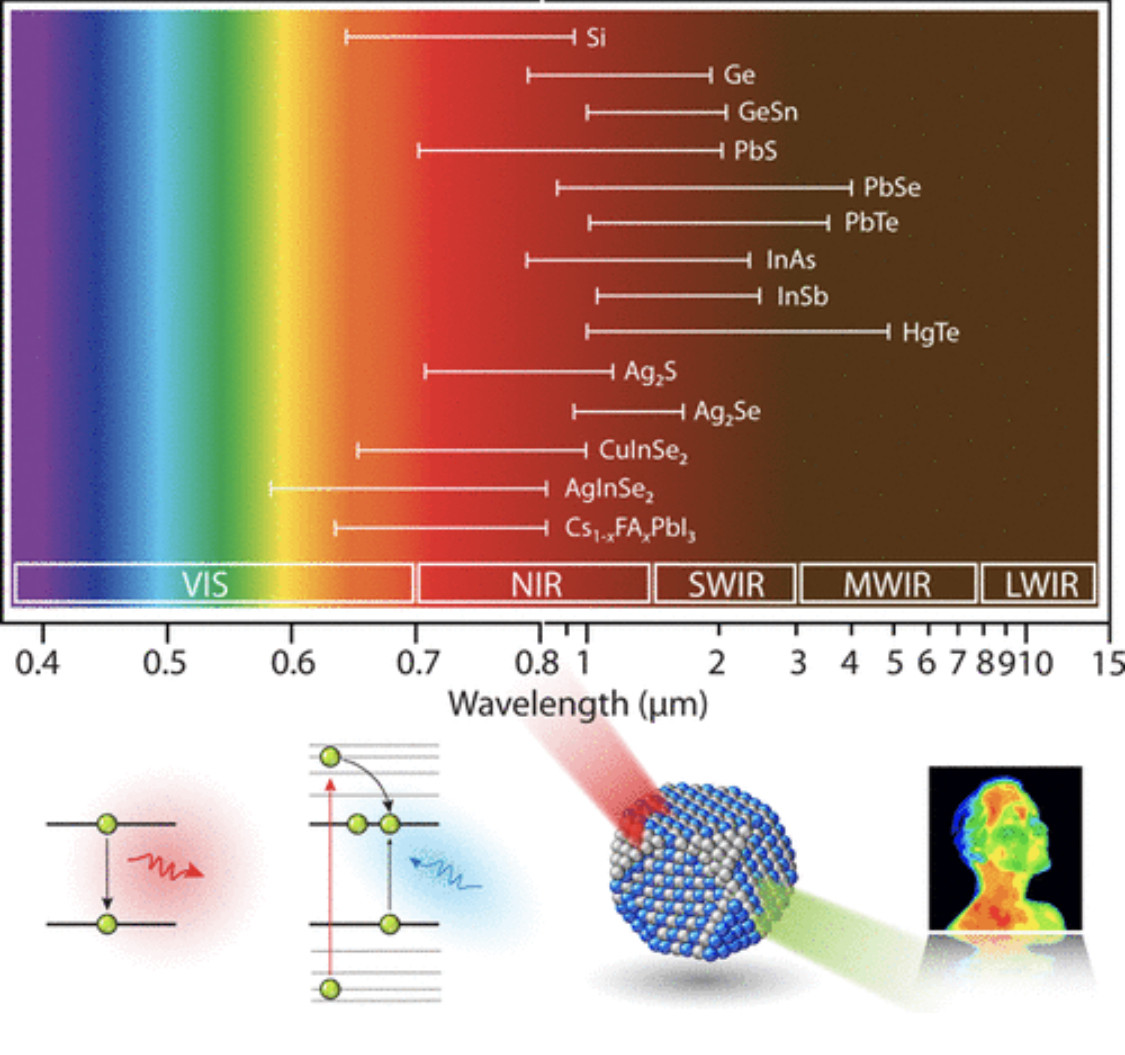
Infrared technologies provide tremendous value to our modern-day society. The need for easy-to-fabricate, solution-processable, tunable infrared active optoelectronic materials has driven the development of infrared colloidal quantum dots, whose band gaps can readily be tuned by dimensional constraints due to the quantum confinement effect. In this Perspective, we summarize recent progress in the development of infrared quantum dots both as infrared light emitters (e.g., in light-emitting diodes, biological imaging, etc.) as well as infrared absorbers (e.g., in photovoltaics, solar fuels, photon up-conversion, etc.), focusing on how fundamental breakthroughs in synthesis, surface chemistry, and characterization techniques are facilitating the implementation of these nanostructures into exploratory device architectures as well as in emerging applications. We discuss the ongoing challenges and opportunities associated with infrared colloidal quantum dots.
Notice: Undefined index: tg1tga_access in /home/admin/www/anonup.com/themes/default/apps/timeline/post.phtml on line 396
The Mac
@TheMac
20 August, 04:51
In response The Mac to his Publication
Plasmonic devices confine light to nanometer-sized regions of space, which turns them into effective cavities for quantum emitters. QDs possess large oscillator strengths and high photostability, making them useful for studies down to the single-particle level.
Notice: Undefined index: tg1tga_access in /home/admin/www/anonup.com/themes/default/apps/timeline/post.phtml on line 396
The Mac
@TheMac
20 August, 04:56
In response The Mac to his Publication
Notice: Undefined index: tg1tga_access in /home/admin/www/anonup.com/themes/default/apps/timeline/post.phtml on line 396
The Mac
@TheMac
20 August, 05:03
In response The Mac to his Publication
Notice: Undefined index: tg1tga_access in /home/admin/www/anonup.com/themes/default/apps/timeline/post.phtml on line 396
The Mac
@TheMac
20 August, 05:04
In response The Mac to his Publication
One of the fastest moving and most exciting interfaces of nanotechnology is the use of quantum dots (QDs) in biology. The unique optical properties of QDs make them appealing as in vivo and in vitro fluorophores in a variety of biological investigations, in which traditional fluorescent labels based on organic molecules fall short of providing long-term stability and simultaneous detection of multiple signals. The ability to make QDs water soluble and target them to specific biomolecules has led to promising applications in cellular labelling, deep-tissue imaging, assay labelling and as efficient fluorescence resonance energy transfer donors.
Notice: Undefined index: tg1tga_access in /home/admin/www/anonup.com/themes/default/apps/timeline/post.phtml on line 396
The Mac
@TheMac
20 August, 05:05
In response The Mac to his Publication
Despite recent progress, much work still needs to be done to achieve reproducible and robust surface functionalization and develop flexible bioconjugation techniques. In this review, we look at current methods for preparing QD bioconjugates as well as presenting an overview of applications. The potential of QDs in biology has just begun to be realized and new avenues will arise as our ability to manipulate these materials improves.
Notice: Undefined index: tg1tga_access in /home/admin/www/anonup.com/themes/default/apps/timeline/post.phtml on line 396
The Mac
@TheMac
20 August, 05:07
In response The Mac to his Publication
We report here a nanostructure that traps single quantum dots for studying strong cavity-emitter coupling. The nanostructure is designed with two elliptical holes in a thin silver patch and a slot that connects the holes. This structure has two functionalities: (1) tweezers for optical trapping; (2) a plasmonic resonant cavity for quantum electrodynamics. The electromagnetic response of the cavity is calculated by finite-difference time-domain (FDTD) simulations, and the optical force is characterized based on the Maxwell’s stress tensor method. To be tweezers, this structure tends to trap quantum dots at the edges of its tips where light is significantly confined.
Notice: Undefined index: tg1tga_access in /home/admin/www/anonup.com/themes/default/apps/timeline/post.phtml on line 396
The Mac
@TheMac
20 August, 05:10
In response The Mac to his Publication
The ability to shape light has revolutionized imaging, optical trapping and both quantum and classical communication. The simultaneous control over both spatio-temporal intensity and polarization structures requires new approaches to optical devices such as meta-materials and -surfaces while at the same time the handedness of structured light lends itself to imaging, probing and manipulating the geometry and potentially chirality of matter. In addition, the generation, propagation and interaction of structured light with matter is governed by topological invariants and conservation laws, which add a complex mathematical component to this exciting and interdisciplinary field.
Notice: Undefined index: tg1tga_access in /home/admin/www/anonup.com/themes/default/apps/timeline/post.phtml on line 396
The Mac
@TheMac
20 August, 05:12
In response The Mac to his Publication
The word interdisciplinary can be broken into its parts: inter-, which means "between" in Latin, and disciplinary, which is from the Latin disciplina and means teaching or knowledge. Interdisciplinary means between fields, but they don't have to be unrelated disciplines.
Notice: Undefined index: tg1tga_access in /home/admin/www/anonup.com/themes/default/apps/timeline/post.phtml on line 396
The Mac
@TheMac
20 August, 05:14
In response The Mac to his Publication
Silicon spin qubits have achieved high-fidelity one- and two-qubit gates1,2,3,4,5, above error-correction thresholds6, promising an industrial route to fault-tolerant quantum computation. A significant next step for the development of scalable multi-qubit processors is the operation of foundry-fabricated, extendable two-dimensional (2D) quantum-dot arrays. In gallium arsenide, 2D arrays recently allowed coherent spin operations and quantum simulations7,8. In silicon, 2D arrays have been limited to transport measurements in the many-electron regime9.
Notice: Undefined index: tg1tga_access in /home/admin/www/anonup.com/themes/default/apps/timeline/post.phtml on line 396
The Mac
@TheMac
20 August, 05:15
In response The Mac to his Publication
Here, we operate a foundry-fabricated 2 × 2 array of silicon quantum dots in the few-electron regime, achieving single-electron occupation in each of the four gate-defined dots, as well as reconfigurable single, double, and triple dots with tunable tunnel couplings. Pulsed-gate and gate-reflectometry techniques permit single-electron manipulation and single-shot charge readout, while the two-dimensionality allows the spatial exchange of electron pairs. The compact form factor of such arrays, whose foundry fabrication can be extended to larger 2 × N arrays, along with the recent demonstration of spin control10,11,12 and spin readout13,14, paves the way for dense qubit arrays for quantum computation and simulation15.
Notice: Undefined index: tg1tga_access in /home/admin/www/anonup.com/themes/default/apps/timeline/post.phtml on line 396
The Mac
@TheMac
20 August, 05:17
In response The Mac to his Publication
The ongoing miniaturization of solid state devices often leads to the question: “How small can we make resistors, transistors, etc., without changing the way they work?” The question can be asked a different way, however: “How small do we have to make devices in order to get fundamentally new properties?” By “new properties” we particularly mean those that arise from quantum mechanics or the quantization of charge in units of e; effects that are only important in small systems such as atoms. “What kind of small electronic devices do we have in mind?” Any sort of clustering of atoms that can be connected to source and drain contacts and whose properties can be regulated with a gate electrode.
Notice: Undefined index: tg1tga_access in /home/admin/www/anonup.com/themes/default/apps/timeline/post.phtml on line 396
The Mac
@TheMac
20 August, 05:17
In response The Mac to his Publication
Practically, the clustering of atoms may be a molecule, a small grain of metallic atoms, or an electronic device that is made with modern chip fabrication techniques. It turns out that such seemingly different structures have quite similar transport properties and that one can explain their physics within one relatively simple framework. In this paper we investigate the physics of electron transport through such small systems.
Notice: Undefined index: tg1tga_access in /home/admin/www/anonup.com/themes/default/apps/timeline/post.phtml on line 396
The Mac
@TheMac
20 August, 05:18
In response The Mac to his Publication
An electron flow is an electric current, the same thing that powers devices such as mobile phones, lights, and computers. Electrons are the negatively charged particles that exist within atoms. Electromagnetic force is responsible for electron flow, and it is one of the four fundamental forces identified by physicists.
Notice: Undefined index: tg1tga_access in /home/admin/www/anonup.com/themes/default/apps/timeline/post.phtml on line 396
The Mac
@TheMac
20 August, 05:20
In response The Mac to his Publication
Sonoluminescence can occur when a sound wave of sufficient intensity induces a gaseous cavity within a liquid to collapse quickly. This cavity may take the form of a pre-existing bubble, or may be generated through a process known as cavitation. Sonoluminescence in the laboratory can be made to be stable, so that a single bubble will expand and collapse over and over again in a periodic fashion, emitting a burst of light each time it collapses. For this to occur, a standing acoustic wave is set up within a liquid, and the bubble will sit at a pressure anti-node of the standing wave. The frequencies of resonance depend on the shape and size of the container in which the bubble is contained.
Notice: Undefined index: tg1tga_access in /home/admin/www/anonup.com/themes/default/apps/timeline/post.phtml on line 396
The Mac
@TheMac
20 August, 05:21
In response The Mac to his Publication
A study describes a method of determining temperatures based on the formation of plasmas. Using argon bubbles in sulfuric acid, the data shows the presence of ionized molecular oxygen O2+, sulfur monoxide, and atomic argon populating high-energy excited states, which confirms a hypothesis that the bubbles have a hot plasma core.[8] The ionization and excitation energy of dioxygenyl cations, which they observed, is 18 electronvolts. From this they conclude the core temperatures reach at least 20,000 kelvins[6]—hotter than the surface of the sun.
Notice: Undefined index: tg1tga_access in /home/admin/www/anonup.com/themes/default/apps/timeline/post.phtml on line 396
The Mac
@TheMac
20 August, 05:23
In response The Mac to his Publication
An electron volt is defined as the amount of kinetic energy acquired by an electron when it is accelerated in an electric field produced by a potential difference of one volt.
Notice: Undefined index: tg1tga_access in /home/admin/www/anonup.com/themes/default/apps/timeline/post.phtml on line 396
The Mac
@TheMac
20 August, 05:24
In response The Mac to his Publication
A particle accelerator is a machine that uses electromagnetic fields to propel charged particles to very high speeds and energies, and to contain them in well-defined beams.
Notice: Undefined index: tg1tga_access in /home/admin/www/anonup.com/themes/default/apps/timeline/post.phtml on line 396
The Mac
@TheMac
20 August, 05:26
In response The Mac to his Publication
An electromagnetic field (also EM field or EMF) is a classical (i.e. non-quantum) field produced by accelerating electric charges.[1] It is the field described by classical electrodynamics and is the classical counterpart to the quantized electromagnetic field tensor in quantum electrodynamics. The electromagnetic field propagates at the speed of light (in fact, this field can be identified as light) and interacts with charges and currents. Its quantum counterpart is one of the four fundamental forces of nature (the others are gravitation, weak interaction and strong interaction.)
Notice: Undefined index: tg1tga_access in /home/admin/www/anonup.com/themes/default/apps/timeline/post.phtml on line 396
The Mac
@TheMac
20 August, 05:27
In response The Mac to his Publication
An electric current is a stream of charged particles, such as electrons or ions, moving through an electrical conductor or space. It is measured as the net rate of flow of electric charge through a surface or into a control volume.[1]: 2 [2]: 622 The moving particles are called charge carriers, which may be one of several types of particles, depending on the conductor. In electric circuits the charge carriers are often electrons moving through a wire. In semiconductors they can be electrons or holes. In an electrolyte the charge carriers are ions, while in plasma, an ionized gas, they are ions and electrons
Notice: Undefined index: tg1tga_access in /home/admin/www/anonup.com/themes/default/apps/timeline/post.phtml on line 396
The Mac
@TheMac
20 August, 05:28
In response The Mac to his Publication
microstream (plural microstreams)
A microscopic stream
A microscopic stream
Notice: Undefined index: tg1tga_access in /home/admin/www/anonup.com/themes/default/apps/timeline/post.phtml on line 396
The Mac
@TheMac
20 August, 05:30
In response The Mac to his Publication
Acoustic microstreaming is another energy released around ultrasonic devices.
Acoustic microstreaming is characterized by the generation of shear forces around the probe immersed in water.
Acoustic microstreaming is characterized by the generation of shear forces around the probe immersed in water.
Notice: Undefined index: tg1tga_access in /home/admin/www/anonup.com/themes/default/apps/timeline/post.phtml on line 396
The Mac
@TheMac
20 August, 05:31
In response The Mac to his Publication
Acoustic streaming is defined as the physical forces of the sound waves that provide a driving force capable of displacing ions and small molecules
Notice: Undefined index: tg1tga_access in /home/admin/www/anonup.com/themes/default/apps/timeline/post.phtml on line 396
Displacement reactions occur when a metal from the electrochemical series is mixed with the ions of a metal lower down in the electrochemical series. The atoms of the more reactive metal push their electrons on to ions of the less reactive metal. An example can be seen below.
05:32 AM - Aug 20, 2022
In response The Mac to his Publication
Only people mentioned by TheMac in this post can reply
The Mac
@TheMac
20 August, 05:35
In response The Mac to his Publication
. . . . . . . . . . . .
wwwwwwwww
. . . . . . . . . . . .
wwwwwwwww
. . . . . . . . . . . .
Notice: Undefined index: tg1tga_access in /home/admin/www/anonup.com/themes/default/apps/timeline/post.phtml on line 396
The Mac
@TheMac
20 August, 05:36
In response The Mac to his Publication
ding (plural dings)
The high-pitched resonant sound of a bell.
The high-pitched resonant sound of a bell.
Notice: Undefined index: tg1tga_access in /home/admin/www/anonup.com/themes/default/apps/timeline/post.phtml on line 396
Linda Moore
@mykismet06350
21 August, 03:38
In response The Mac to his Publication
Matthew 12 :12 How much more valuable is a man than a sheep! Therefore it is lawful to do good on the Sabbath.” Then Jesus said to the man, “Stretch out your hand.” So he stretched it out, and it was restored to full use, just like the other.…
Notice: Undefined index: tg1tga_access in /home/admin/www/anonup.com/themes/default/apps/timeline/post.phtml on line 396