The Mac
@TheMac
26 September, 05:06
Notice: Undefined index: tg1tga_access in /home/admin/www/anonup.com/themes/default/apps/timeline/post.phtml on line 396
The Mac
@TheMac
26 September, 05:11
In response The Mac to his Publication
Father, forgive them; for they know not what they do.
Notice: Undefined index: tg1tga_access in /home/admin/www/anonup.com/themes/default/apps/timeline/post.phtml on line 396
The Mac
@TheMac
26 September, 05:14
In response The Mac to his Publication
COVID-19 and Brain Injury. COVID-19 may lead to changes in personality and behavior, which require treatment across the continuum of care. Traumatic brain injury, stroke, anoxic brain injury, encephalitis, and other neurological conditions leading to brain insult can be devastating to individuals and those close to them ( Table 1 ).
Notice: Undefined index: tg1tga_access in /home/admin/www/anonup.com/themes/default/apps/timeline/post.phtml on line 396
The Mac
@TheMac
26 September, 05:16
In response The Mac to his Publication
Brain injury due to oxygen deficiency Lightning or Electric shock
Notice: Undefined index: tg1tga_access in /home/admin/www/anonup.com/themes/default/apps/timeline/post.phtml on line 396
The Mac
@TheMac
26 September, 05:22
In response The Mac to his Publication
Notice: Undefined index: tg1tga_access in /home/admin/www/anonup.com/themes/default/apps/timeline/post.phtml on line 396
The Mac
@TheMac
26 September, 05:22
In response The Mac to his Publication
An oxidizing agent (also known as an oxidant, oxidizer, electron recipient, or electron acceptor) is a substance in a redox chemical reaction that gains or "accepts"/"receives" an electron from a reducing agent (called the reductant, reducer, or electron donor). In other words, an oxidizer is any substance that oxidizes another substance. The oxidation state, which describes the degree of loss of electrons, of the oxidizer decreases while that of the reductant increases; this is expressed by saying that oxidizers "undergo reduction" and "are reduced" while reducers "undergo oxidation" and "are oxidized". Common oxidizing agents are oxygen, hydrogen peroxide and the halogens.
Notice: Undefined index: tg1tga_access in /home/admin/www/anonup.com/themes/default/apps/timeline/post.phtml on line 396
The Mac
@TheMac
26 September, 05:23
In response The Mac to his Publication
Notice: Undefined index: tg1tga_access in /home/admin/www/anonup.com/themes/default/apps/timeline/post.phtml on line 396
The Mac
@TheMac
26 September, 05:24
In response The Mac to his Publication
In one sense, an oxidizing agent is a chemical species that undergoes a chemical reaction in which it gains one or more electrons. In that sense, it is one component in an oxidation–reduction (redox) reaction. In the second sense, an oxidizing agent is a chemical species that transfers electronegative atoms, usually oxygen, to a substrate. Combustion, many explosives, and organic redox reactions involve atom-transfer reactions.
Notice: Undefined index: tg1tga_access in /home/admin/www/anonup.com/themes/default/apps/timeline/post.phtml on line 396
The Mac
@TheMac
26 September, 05:25
In response The Mac to his Publication
In a combustion reaction, a fuel is heated and it reacts with oxygen. The fire triangle summarises the three things needed for combustion - a fuel, heat and oxygen.
Notice: Undefined index: tg1tga_access in /home/admin/www/anonup.com/themes/default/apps/timeline/post.phtml on line 396
The Mac
@TheMac
26 September, 05:26
In response The Mac to his Publication
In physics, a photon gas is a gas-like collection of photons, which has many of the same properties of a conventional gas like hydrogen or neon – including pressure, temperature, and entropy. The most common example of a photon gas in equilibrium is the black-body radiation.
Notice: Undefined index: tg1tga_access in /home/admin/www/anonup.com/themes/default/apps/timeline/post.phtml on line 396
The Mac
@TheMac
26 September, 05:30
In response The Mac to his Publication
Electron acceptors participate in electron-transfer reactions. In this context, the oxidizing agent is called an electron acceptor and the reducing agent is called an electron donor. A classic oxidizing agent is the ferrocenium ion Fe(C
5H
5)+
2, which accepts an electron to form Fe(C5H5)2. One of the strongest acceptors commercially available is "Magic blue", the radical cation derived from N(C6H4-4-Br)3.[2]
Extensive tabulations of ranking the electron accepting properties of various reagents (redox potentials) are available, see Standard electrode potential (data page).
5H
5)+
2, which accepts an electron to form Fe(C5H5)2. One of the strongest acceptors commercially available is "Magic blue", the radical cation derived from N(C6H4-4-Br)3.[2]
Extensive tabulations of ranking the electron accepting properties of various reagents (redox potentials) are available, see Standard electrode potential (data page).
Notice: Undefined index: tg1tga_access in /home/admin/www/anonup.com/themes/default/apps/timeline/post.phtml on line 396
The Mac
@TheMac
26 September, 06:10
In response The Mac to his Publication
Molecular doping of organic semiconductors is a powerful tool for the optimization of organic electronic devices and organic thermoelectric materials. However, there are few redox dopants that have a sufficiently high electron affinity to allow the doping of conjugated polymers with an ionization energy of more than 5.3 eV. Here, p-doping of a broad palette of conjugated polymers with high ionization energies is achieved by using the strong oxidant tris(4-bromophenyl)ammoniumyl hexachloroantimonate (Magic Blue). In particular diketopyrrolopyrrole (DPP)-based copolymers reach a conductivity of up to 100 S cm−1 and a thermoelectric power factor of 10 µW m−1 K−2. Further, both electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) as well as a combination of spectroelectrochemistry and chronoamperometry is used to estimate the charge-carrier density of the polymer PDPP-3T doped with Magic Blue.
Notice: Undefined index: tg1tga_access in /home/admin/www/anonup.com/themes/default/apps/timeline/post.phtml on line 396
The Mac
@TheMac
26 September, 06:10
In response The Mac to his Publication
A molar attenuation coefficient of 6.0 ± 0.2 × 103 m2 mol−1 is obtained for the first polaronic sub-bandgap absorption of electrochemically oxidized PDPP-3T. Comparison with chemically doped PDPP-3T suggests a charge-carrier density on the order of 1026 m−3, which yields a charge-carrier mobility of up to 0.5 cm2 V−1 s−1 for the most heavily doped material.
Notice: Undefined index: tg1tga_access in /home/admin/www/anonup.com/themes/default/apps/timeline/post.phtml on line 396
The Mac
@TheMac
26 September, 06:13
In response The Mac to his Publication
Notice: Undefined index: tg1tga_access in /home/admin/www/anonup.com/themes/default/apps/timeline/post.phtml on line 396
The Mac
@TheMac
26 September, 06:15
In response The Mac to his Publication
In semiconductor production, doping is the intentional introduction of impurities into an intrinsic semiconductor for the purpose of modulating its electrical, optical and structural properties. The doped material is referred to as an extrinsic semiconductor.
Small numbers of dopant atoms can change the ability of a semiconductor to conduct electricity. When on the order of one dopant atom is added per 100 million atoms, the doping is said to be low or light. When many more dopant atoms are added, on the order of one per ten thousand atoms, the doping is referred to as high or heavy.
Small numbers of dopant atoms can change the ability of a semiconductor to conduct electricity. When on the order of one dopant atom is added per 100 million atoms, the doping is said to be low or light. When many more dopant atoms are added, on the order of one per ten thousand atoms, the doping is referred to as high or heavy.
Notice: Undefined index: tg1tga_access in /home/admin/www/anonup.com/themes/default/apps/timeline/post.phtml on line 396
The Mac
@TheMac
26 September, 06:15
In response The Mac to his Publication
This is often shown as n+ for n-type doping or p+ for p-type doping. (See the article on semiconductors for a more detailed description of the doping mechanism.) A semiconductor doped to such high levels that it acts more like a conductor than a semiconductor is referred to as a degenerate semiconductor. A semiconductor can be considered i-type semiconductor if it has been doped in equal quantities of p and n.
In the context of phosphors and scintillators, doping is better known as activation; this is not to be confused with dopant activation in semiconductors. Doping is also used to control the color in some pigments.
In the context of phosphors and scintillators, doping is better known as activation; this is not to be confused with dopant activation in semiconductors. Doping is also used to control the color in some pigments.
Notice: Undefined index: tg1tga_access in /home/admin/www/anonup.com/themes/default/apps/timeline/post.phtml on line 396
The Mac
@TheMac
26 September, 08:07
In response The Mac to his Publication
Notice: Undefined index: tg1tga_access in /home/admin/www/anonup.com/themes/default/apps/timeline/post.phtml on line 396
The Mac
@TheMac
26 September, 08:10
In response The Mac to his Publication
Notice: Undefined index: tg1tga_access in /home/admin/www/anonup.com/themes/default/apps/timeline/post.phtml on line 396
The Mac
@TheMac
26 September, 08:10
In response The Mac to his Publication
Notice: Undefined index: tg1tga_access in /home/admin/www/anonup.com/themes/default/apps/timeline/post.phtml on line 396
The Mac
@TheMac
26 September, 08:13
In response The Mac to his Publication
Notice: Undefined index: tg1tga_access in /home/admin/www/anonup.com/themes/default/apps/timeline/post.phtml on line 396
The Mac
@TheMac
26 September, 08:14
In response The Mac to his Publication
Notice: Undefined index: tg1tga_access in /home/admin/www/anonup.com/themes/default/apps/timeline/post.phtml on line 396
The Mac
@TheMac
26 September, 08:14
In response The Mac to his Publication
Notice: Undefined index: tg1tga_access in /home/admin/www/anonup.com/themes/default/apps/timeline/post.phtml on line 396
The Mac
@TheMac
26 September, 08:16
In response The Mac to his Publication
Notice: Undefined index: tg1tga_access in /home/admin/www/anonup.com/themes/default/apps/timeline/post.phtml on line 396
The Mac
@TheMac
26 September, 08:18
In response The Mac to his Publication
Spintronics (a portmanteau meaning spin transport electronics[1][2][3]), also known as spin electronics, is the study of the intrinsic spin of the electron and its associated magnetic moment, in addition to its fundamental electronic charge, in solid-state devices.[4] The field of spintronics concerns spin-charge coupling in metallic systems; the analogous effects in insulators fall into the field of multiferroics.
Spintronics fundamentally differs from traditional electronics in that, in addition to charge state, electron spins are exploited as a further degree of freedom, with implications in the efficiency of data storage and transfer. Spintronic systems are most often realised in dilute magnetic semiconductors (DMS) and Heusler alloys and are of particular interest in the field of quantum computing and neuromorphic computing.
Spintronics fundamentally differs from traditional electronics in that, in addition to charge state, electron spins are exploited as a further degree of freedom, with implications in the efficiency of data storage and transfer. Spintronic systems are most often realised in dilute magnetic semiconductors (DMS) and Heusler alloys and are of particular interest in the field of quantum computing and neuromorphic computing.
Notice: Undefined index: tg1tga_access in /home/admin/www/anonup.com/themes/default/apps/timeline/post.phtml on line 396
The Mac
@TheMac
26 September, 08:41
In response The Mac to his Publication
Neuromorphic engineering, also known as neuromorphic computing,[1][2][3] is the use of very-large-scale integration (VLSI) systems containing electronic analog circuits to mimic neuro-biological architectures present in the nervous system. A neuromorphic computer/chip is any device that uses physical artificial neurons (made from silicon) to do computations.[4][5] In recent times, the term neuromorphic has been used to describe analog, digital, mixed-mode analog/digital VLSI, and software systems that implement models of neural systems (for perception, motor control, or multisensory integration).
Notice: Undefined index: tg1tga_access in /home/admin/www/anonup.com/themes/default/apps/timeline/post.phtml on line 396
The Mac
@TheMac
26 September, 08:42
In response The Mac to his Publication
The implementation of neuromorphic computing on the hardware level can be realized by oxide-based memristors,[6] spintronic memories, threshold switches, and transistors.[7][5] Training software-based neuromorphic systems of spiking neural networks can be achieved using error backpropagation, e.g., using Python based frameworks such as snnTorch,[8] or using canonical learning rules from the biological learning literature, e.g., using BindsNet.[9]
Notice: Undefined index: tg1tga_access in /home/admin/www/anonup.com/themes/default/apps/timeline/post.phtml on line 396
The Mac
@TheMac
26 September, 08:44
In response The Mac to his Publication
A memristor (/ˈmɛmrɪstər/; a portmanteau of memory resistor) is a non-linear two-terminal electrical component relating electric charge and magnetic flux linkage. It was described and named in 1971 by Leon Chua, completing a theoretical quartet of fundamental electrical components which comprises also the resistor, capacitor and inductor.
Notice: Undefined index: tg1tga_access in /home/admin/www/anonup.com/themes/default/apps/timeline/post.phtml on line 396
The Mac
@TheMac
26 September, 08:50
In response The Mac to his Publication
Chua and Kang later generalized the concept to memristive systems.[2] Such a system comprises a circuit, of multiple conventional components, which mimics key properties of the ideal memristor component and is also commonly referred to as a memristor. Several such memristor system technologies have been developed, notably ReRAM.
The identification of memristive properties in electronic devices has attracted controversy. Experimentally, the ideal memristor has yet to be demonstrated.[3][4]
The identification of memristive properties in electronic devices has attracted controversy. Experimentally, the ideal memristor has yet to be demonstrated.[3][4]
Notice: Undefined index: tg1tga_access in /home/admin/www/anonup.com/themes/default/apps/timeline/post.phtml on line 396
The Mac
@TheMac
26 September, 08:52
In response The Mac to his Publication
Notice: Undefined index: tg1tga_access in /home/admin/www/anonup.com/themes/default/apps/timeline/post.phtml on line 396
The Mac
@TheMac
26 September, 09:05
In response The Mac to his Publication
Colonialism in Africa
Amit Chitnis, Diana Rawls, and Jim Moore proposed that HIV may have emerged epidemically as a result of harsh conditions, forced labor, displacement, and unsafe injection and vaccination practices associated with colonialism, particularly in French Equatorial Africa.[30] The workers in plantations, construction projects, and other colonial enterprises were supplied with bushmeat, which would have contributed to an increase in hunting and, it follows, a higher incidence of human exposure to SIV. Several historical sources support the view that bushmeat hunting indeed increased, both because of the necessity to supply workers and because firearms became more widely available.[30][31][32]
Amit Chitnis, Diana Rawls, and Jim Moore proposed that HIV may have emerged epidemically as a result of harsh conditions, forced labor, displacement, and unsafe injection and vaccination practices associated with colonialism, particularly in French Equatorial Africa.[30] The workers in plantations, construction projects, and other colonial enterprises were supplied with bushmeat, which would have contributed to an increase in hunting and, it follows, a higher incidence of human exposure to SIV. Several historical sources support the view that bushmeat hunting indeed increased, both because of the necessity to supply workers and because firearms became more widely available.[30][31][32]
Notice: Undefined index: tg1tga_access in /home/admin/www/anonup.com/themes/default/apps/timeline/post.phtml on line 396
The Mac
@TheMac
26 September, 09:06
In response The Mac to his Publication
The colonial authorities also gave many vaccinations against smallpox, and injections, of which many would be made without sterilising the equipment between uses. Chitnis et al. proposed that both these parenteral risks and the prostitution associated with forced labor camps could have caused serial transmission (or serial passage) of SIV between humans (see discussion of this in the next section).[30]
Notice: Undefined index: tg1tga_access in /home/admin/www/anonup.com/themes/default/apps/timeline/post.phtml on line 396
The Mac
@TheMac
27 September, 02:01
In response The Mac to his Publication
Notice: Undefined index: tg1tga_access in /home/admin/www/anonup.com/themes/default/apps/timeline/post.phtml on line 396
The Mac
@TheMac
27 September, 02:04
In response The Mac to his Publication
Bullshitter’s?
Notice: Undefined index: tg1tga_access in /home/admin/www/anonup.com/themes/default/apps/timeline/post.phtml on line 396
The Mac
@TheMac
27 September, 02:05
In response The Mac to his Publication
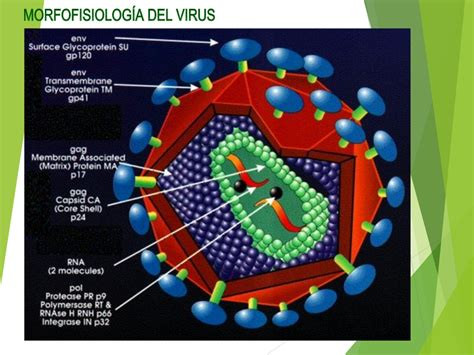
A nanoparticle or ultrafine particle is usually defined as a particle of matter that is between 1 and 100 nanometres (nm) in diameter.[1][2] The term is sometimes used for larger particles, up to 500 nm,[citation needed] or fibers and tubes that are less than 100 nm in only two directions.[3] At the lowest range, metal particles smaller than 1 nm are usually called atom clusters instead.
Notice: Undefined index: tg1tga_access in /home/admin/www/anonup.com/themes/default/apps/timeline/post.phtml on line 396
The Mac
@TheMac
27 September, 02:05
In response The Mac to his Publication
The lipid bilayer (or phospholipid bilayer) is a thin polar membrane made of two layers of lipid molecules. These membranes are flat sheets that form a continuous barrier around all cells. The cell membranes of almost all organisms and many viruses are made of a lipid bilayer, as are the nuclear membrane surrounding the cell nucleus, and membranes of the membrane-bound organelles in the cell. The lipid bilayer is the barrier that keeps ions, proteins and other molecules where they are needed and prevents them from diffusing into areas where they should not be. Lipid bilayers are ideally suited to this role, even though they are only a few nanometers in width,[1] because they are impermeable to most water-soluble (hydrophilic) molecules. Bilayers are particularly impermeable to ions, which allows cells to regulate salt concentrations and pH by transporting ions across their membranes using proteins called ion pumps.
Notice: Undefined index: tg1tga_access in /home/admin/www/anonup.com/themes/default/apps/timeline/post.phtml on line 396
The Mac
@TheMac
27 September, 02:47
In response The Mac to his Publication
phototriggerable (not comparable)
photochemically triggerable
photochemically triggerable
Notice: Undefined index: tg1tga_access in /home/admin/www/anonup.com/themes/default/apps/timeline/post.phtml on line 396
The Mac
@TheMac
27 September, 02:49
In response The Mac to his Publication
When working with liposomes analogous to cell membranes, it is important to develop substrates that can regulate interactions with the liposome surface in response to light. We achieved a photo-triggered release from liposomes by using a copolymer of poly(vinyl alcohol) carrying a malachite green moiety (PVAMG). Although PVAMG is a neutral polymer under dark conditions, it is photoionized upon exposure to UV light, resulting in the formation of a cationic site for binding to liposomes with a negatively charged surface.
Notice: Undefined index: tg1tga_access in /home/admin/www/anonup.com/themes/default/apps/timeline/post.phtml on line 396
The Mac
@TheMac
27 September, 02:49
In response The Mac to his Publication
Under UV irradiation, PVAMG showed effective interaction with liposomes, releasing the encapsulated compound; however, this release was negligible under dark conditions. The poly(vinyl alcohol) moiety of PVAMG played an important role in the photo-triggered release. This release was caused by membrane destabilization without lipid solubilization. We also investigated different aspects of liposome/PVAMG interactions, including PVAMG-induced fusion between the liposomes and the change in the liposome morphologies.
Keywords: Binding; Copolymer; Liposome; Malachite green; Photoionization; Release.
Keywords: Binding; Copolymer; Liposome; Malachite green; Photoionization; Release.
Notice: Undefined index: tg1tga_access in /home/admin/www/anonup.com/themes/default/apps/timeline/post.phtml on line 396
The Mac
@TheMac
27 September, 02:50
In response The Mac to his Publication
photo-triggered release.
Notice: Undefined index: tg1tga_access in /home/admin/www/anonup.com/themes/default/apps/timeline/post.phtml on line 396
The Mac
@TheMac
27 September, 02:51
In response The Mac to his Publication
This review summarizes articles that have been reported in literature on liposome-based strategies for effective drug delivery across the blood–brain barrier. Due to their unique physicochemical characteristics, liposomes have been widely investigated for their application in drug delivery and in vivo bioimaging for the treatment and/or diagnosis of neurological diseases, such as Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, stroke, and glioma. Several strategies have been used to deliver drug and/or imaging agents to the brain. Covalent ligation of such macromolecules as peptides, antibodies, and RNA aptamers is an effective method for receptor-targeting liposomes, which allows their blood–brain barrier penetration and/or the delivery of their therapeutic molecule specifically to the disease site.
Notice: Undefined index: tg1tga_access in /home/admin/www/anonup.com/themes/default/apps/timeline/post.phtml on line 396
The Mac
@TheMac
27 September, 02:51
In response The Mac to his Publication
Additionally, methods have been employed for the development of liposomes that can respond to external stimuli. It can be concluded that the development of liposomes for brain delivery is still in its infancy, although these systems have the potential to revolutionize the ways in which medicine is administered.
Keywords: Alzheimer, Parkinson, stroke, cerebral ischemia, glioma, liposomes, blood–brain barrier
Keywords: Alzheimer, Parkinson, stroke, cerebral ischemia, glioma, liposomes, blood–brain barrier
Notice: Undefined index: tg1tga_access in /home/admin/www/anonup.com/themes/default/apps/timeline/post.phtml on line 396
The Mac
@TheMac
27 September, 02:52
In response The Mac to his Publication
external stimuli
noun
A signal (stimulus) that originates from outside an organism.
noun
A signal (stimulus) that originates from outside an organism.
Notice: Undefined index: tg1tga_access in /home/admin/www/anonup.com/themes/default/apps/timeline/post.phtml on line 396
The Mac
@TheMac
27 September, 02:53
In response The Mac to his Publication
The blood-brain barrier (BBB) is formed by tightly connected cerebrovascular endothelial cells, but its normal function also depends on paracrine interactions between the brain endothelium and closely located glia. There is a growing consensus that brain injury, whether it is ischemic, hemorrhagic, or traumatic, leads to dysfunction of the BBB. Changes in BBB function observed after injury are thought to contribute to the loss of neural tissue and to affect the response to neuroprotective drugs. New discoveries suggest that considering the entire gliovascular unit, rather than the BBB alone, will expand our understanding of the cellular and molecular responses to traumatic brain injury (TBI).
Notice: Undefined index: tg1tga_access in /home/admin/www/anonup.com/themes/default/apps/timeline/post.phtml on line 396
The Mac
@TheMac
27 September, 02:54
In response The Mac to his Publication
This review will address the BBB breakdown in TBI, the role of blood-borne factors in affecting the function of the gliovascular unit, changes in BBB permeability and post-traumatic edema formation, and the major pathophysiological factors associated with TBI that may contribute to post-traumatic dysfunction of the BBB. The key role of neuroinflammation and the possible effect of injury on transport mechanisms at the BBB will also be described. Finally, the potential role of the BBB as a target for therapeutic intervention through restoration of normal BBB function after injury and/or by harnessing the cerebrovascular endothelium to produce neurotrophic growth factors will be discussed.
Keywords: Blood-brain barrier, Gliovascular unit, Traumatic brain injury
Keywords: Blood-brain barrier, Gliovascular unit, Traumatic brain injury
Notice: Undefined index: tg1tga_access in /home/admin/www/anonup.com/themes/default/apps/timeline/post.phtml on line 396
The Mac
@TheMac
27 September, 02:55
In response The Mac to his Publication
BBB breakdown is associated with more rapid cognitive decline. Inflammatory mechanisms, including cell adhesion, neutrophil migration, lipid metabolism, and angiogenesis may be implicated.
Notice: Undefined index: tg1tga_access in /home/admin/www/anonup.com/themes/default/apps/timeline/post.phtml on line 396
The Mac
@TheMac
27 September, 02:56
In response The Mac to his Publication
Notice: Undefined index: tg1tga_access in /home/admin/www/anonup.com/themes/default/apps/timeline/post.phtml on line 396
The Mac
@TheMac
27 September, 02:57
In response The Mac to his Publication
Conclusion: All vaccines can cause neuroinflammation.
Notice: Undefined index: tg1tga_access in /home/admin/www/anonup.com/themes/default/apps/timeline/post.phtml on line 396
The Mac
@TheMac
27 September, 02:59
In response The Mac to his Publication
Every year, approximately 1.4 million US citizens visit emergency rooms for traumatic brain injuries. Formerly known as an acute injury, chronic neurodegenerative symptoms such as compromised motor skills, decreased cognitive abilities, and emotional and behavioral changes have caused the scientific community to consider chronic aspects of the disorder. The injury causing impact prompts multiple cell death processes, starting with neuronal necrosis, and progressing to various secondary cell death mechanisms. Secondary cell death mechanisms, including excitotoxicity, oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, blood-brain barrier disruption, and inflammation accompany chronic traumatic brain injury (TBI) and often contribute to long-term disabilities.
One hallmark of both acute and chronic TBI is neuroinflammation.
One hallmark of both acute and chronic TBI is neuroinflammation.
Notice: Undefined index: tg1tga_access in /home/admin/www/anonup.com/themes/default/apps/timeline/post.phtml on line 396
The Mac
@TheMac
27 September, 03:00
In response The Mac to his Publication
Pedophilia, aka pedophilic disorder, could have many causes, including genetics, hormones, and structural brain changes.
Notice: Undefined index: tg1tga_access in /home/admin/www/anonup.com/themes/default/apps/timeline/post.phtml on line 396
The Mac
@TheMac
27 September, 03:01
In response The Mac to his Publication
When he began making sexual advances towards his young stepdaughter, he was legally removed from the home and diagnosed with paedophilia. Later, it was discovered that he had a brain tumour displacing part of his orbitofrontal cortex, disrupting its function. The symptoms resolved with the removal of the tumour.
Notice: Undefined index: tg1tga_access in /home/admin/www/anonup.com/themes/default/apps/timeline/post.phtml on line 396
The Mac
@TheMac
27 September, 03:02
In response The Mac to his Publication
Eukaryotic cells have developed complex systems to regulate the production and response to reactive oxygen species (ROS). Different ROS control diverse aspects of cell behaviour from signalling to death, and deregulation of ROS production and ROS limitation pathways are common features of cancer cells.
Notice: Undefined index: tg1tga_access in /home/admin/www/anonup.com/themes/default/apps/timeline/post.phtml on line 396
The Mac
@TheMac
27 September, 03:04
In response The Mac to his Publication
The unique physicochemical characteristics of nanoparticles have recently gained increasing attention in a diverse set of applications, particularly in the biomedical field. However, concerns about the potential toxicological effects of nanoparticles remain, as they have a higher tendency to generate excessive amounts of reactive oxygen species (ROS).
Notice: Undefined index: tg1tga_access in /home/admin/www/anonup.com/themes/default/apps/timeline/post.phtml on line 396
The Mac
@TheMac
27 September, 03:04
In response The Mac to his Publication
Due to the strong oxidation potential, the excess ROS induced by nanoparticles can result in the damage of biomolecules and organelle structures and lead to protein oxidative carbonylation, lipid peroxidation, DNA/RNA breakage, and membrane structure destruction, which further cause necrosis, apoptosis, or even mutagenesis. This review aims to give a summary of the mechanisms and responsible for ROS generation by nanoparticles at the cellular level and provide insights into the mechanics of ROS-mediated biotoxicity. We summarize the literature on nanoparticle toxicity and suggest strategies to optimize nanoparticles for biomedical applications.
Notice: Undefined index: tg1tga_access in /home/admin/www/anonup.com/themes/default/apps/timeline/post.phtml on line 396
The Mac
@TheMac
27 September, 03:05
In response The Mac to his Publication
The rapidly emerging field of nanotechnology has offered innovative discoveries in the medical, industrial, and consumer sectors. The unique physicochemical and electrical properties of engineered nanoparticles (NP) make them highly desirable in a variety of applications. However, these novel properties of NP are fraught with concerns for environmental and occupational exposure. Changes in structural and physicochemical properties of NP can lead to changes in biological activities including ROS generation, one of the most frequently reported NP-associated toxicities.
Notice: Undefined index: tg1tga_access in /home/admin/www/anonup.com/themes/default/apps/timeline/post.phtml on line 396
The Mac
@TheMac
27 September, 03:06
In response The Mac to his Publication
Oxidative stress induced by engineered NP is due to acellular factors such as particle surface, size, composition, and presence of metals, while cellular responses such as mitochondrial respiration, NP-cell interaction, and immune cell activation are responsible for ROS-mediated damage. NP-induced oxidative stress responses are torch bearers for further pathophysiological effects including genotoxicity, inflammation, and fibrosis as demonstrated by activation of associated cell signaling pathways. Since oxidative stress is a key determinant of NP-induced injury, it is necessary to characterize the ROS response resulting from NP. Through physicochemical characterization and understanding of the multiple signaling cascades activated by NP-induced ROS, a systemic toxicity screen with oxidative stress as a predictive model for NP-induced injury can be developed.
Notice: Undefined index: tg1tga_access in /home/admin/www/anonup.com/themes/default/apps/timeline/post.phtml on line 396
The Mac
@TheMac
27 September, 03:07
In response The Mac to his Publication
Nanoscale drug delivery systems using liposomes and nanoparticles are emerging technologies for the rational delivery of chemotherapeutic drugs in the treatment of cancer. Their use offers improved pharmacokinetic properties, controlled and sustained release of drugs and, more importantly, lower systemic toxicity. The commercial availability of liposomal Doxil and albumin-nanoparticle-based Abraxane has focused attention on this innovative and exciting field. Recent advances in liposome technology offer better treatment of multidrug-resistant cancers and lower cardiotoxicity. Nanoparticles offer increased precision in chemotherapeutic targeting of prostate cancer and new avenues for the treatment of breast cancer. Here we review current knowledge on the two technologies and their potential applications to cancer treatment.
Notice: Undefined index: tg1tga_access in /home/admin/www/anonup.com/themes/default/apps/timeline/post.phtml on line 396
The Mac
@TheMac
27 September, 03:09
In response The Mac to his Publication
Nowadays more than thousands of different nanoparticles are known, though no well-defined guidelines to evaluate their potential toxicity and to control their exposure are fully provided. The way of entry of nanoparticles together with their specificities such as chemistry, chemical composition, size, shape or morphology, surface charge and area can influence their biological activities and effects. A specific property may give rise to either a safe particle or to a dangerous one. The small size allows nanoparticles to enter the body by crossing several barriers, to pass into the blood stream and lymphatic system from where they can reach organs and tissues and strictly interact with biological structures, thus damaging their normal functions in different ways.
Notice: Undefined index: tg1tga_access in /home/admin/www/anonup.com/themes/default/apps/timeline/post.phtml on line 396
The Mac
@TheMac
27 September, 03:18
In response The Mac to his Publication
Pure Genius
Bruce Miller directs the UCSF Memory and Aging Center in San Francisco, where as a behavioral neurologist he treats elderly people stricken with Alzheimer’s disease and late-life psychosis. One day in the mid-1990s, the son of a patient pointed out his father’s new obsession with painting. As his father’s symptoms worsened, the man said, his paintings improved. Soon, Miller began to identify other patients who displayed unexpected new talents as their neurological degeneration continued. As dementia laid waste to brain regions associated with language, higher-order processing, and social norms, their artistic abilities exploded.
Bruce Miller directs the UCSF Memory and Aging Center in San Francisco, where as a behavioral neurologist he treats elderly people stricken with Alzheimer’s disease and late-life psychosis. One day in the mid-1990s, the son of a patient pointed out his father’s new obsession with painting. As his father’s symptoms worsened, the man said, his paintings improved. Soon, Miller began to identify other patients who displayed unexpected new talents as their neurological degeneration continued. As dementia laid waste to brain regions associated with language, higher-order processing, and social norms, their artistic abilities exploded.
Notice: Undefined index: tg1tga_access in /home/admin/www/anonup.com/themes/default/apps/timeline/post.phtml on line 396
The Mac
@TheMac
27 September, 03:19
In response The Mac to his Publication
Though these symptoms defied conventional wisdom on brain disease in the elderly—artists afflicted with Alzheimer’s typically lose artistic ability—Miller realized they were consistent with another population described in the literature: savants. That wasn’t the only similarity. Savants often display an obsessive compulsion to perform their special skill, and they exhibit deficits in social and language behaviors, defects present in dementia patients. Miller wondered if there might be neurological similarities too. Although the exact mechanisms at work in the brains of savants have never been identified and can vary from case to case, several studies dating back to at least the 1970s have found left-hemispheric damage in autistic savants with prodigious artistic, mathematical, and memory skills.
Notice: Undefined index: tg1tga_access in /home/admin/www/anonup.com/themes/default/apps/timeline/post.phtml on line 396
The Mac
@TheMac
27 September, 03:21
In response The Mac to his Publication
Miller decided to find out precisely where in the left hemisphere of regular savants—whose skills usually become apparent at a very young age—these defects existed. He read the brain scan of a five-year-old autistic savant able to reproduce intricate scenes from memory on an Etch-a-Sketch. Single-photon-emission computed tomography (SPECT) showed abnormal inactivity in the anterior temporal lobes of the left hemisphere—exactly the results he found in his dementia patients.
Notice: Undefined index: tg1tga_access in /home/admin/www/anonup.com/themes/default/apps/timeline/post.phtml on line 396
The Mac
@TheMac
27 September, 03:26
In response The Mac to his Publication
If you’ve ever dealt with someone who has had a traumatic brain injury or TBI, you may already know that one of the first and most prominently displayed symptoms tends to be a problem with anger; that is, someone affected by a TBI may display anger more rapidly and intensely than prior to the injury.
Notice: Undefined index: tg1tga_access in /home/admin/www/anonup.com/themes/default/apps/timeline/post.phtml on line 396
While a traumatic brain injury (TBI) and narcissistic personality disorder (NPD) are not directly linked, the symptoms may appear to be nearly identical, and in some cases, personality disorders can be developed as a side-effect of the TBI.
03:26 AM - Sep 27, 2022
In response The Mac to his Publication
Only people mentioned by TheMac in this post can reply
The Mac
@TheMac
27 September, 03:28
In response The Mac to his Publication
Narcissistic personality disorder (NPD) is a mental disorder characterized by a life-long pattern of exaggerated feelings of self-importance, an excessive need for admiration, a diminished ability to empathize with others' feelings, and (often) psychologically abusive behavior. Narcissistic personality disorder is one of the sub-types of the broader category known as personality disorders. It is often comorbid with other mental disorders and associated with significant functional impairment and psychosocial disability.
Notice: Undefined index: tg1tga_access in /home/admin/www/anonup.com/themes/default/apps/timeline/post.phtml on line 396
The Mac
@TheMac
27 September, 03:30
In response The Mac to his Publication
A new study regarding Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) and schizophrenia has researchers taking a second look at the link between TBI and schizophrenia. The study shows that those who suffer a brain injury may also be at a higher risk for schizophrenia. The problem is worse in patients with a genetic risk for the mental disorder.
Notice: Undefined index: tg1tga_access in /home/admin/www/anonup.com/themes/default/apps/timeline/post.phtml on line 396